How disc brakes work
structure
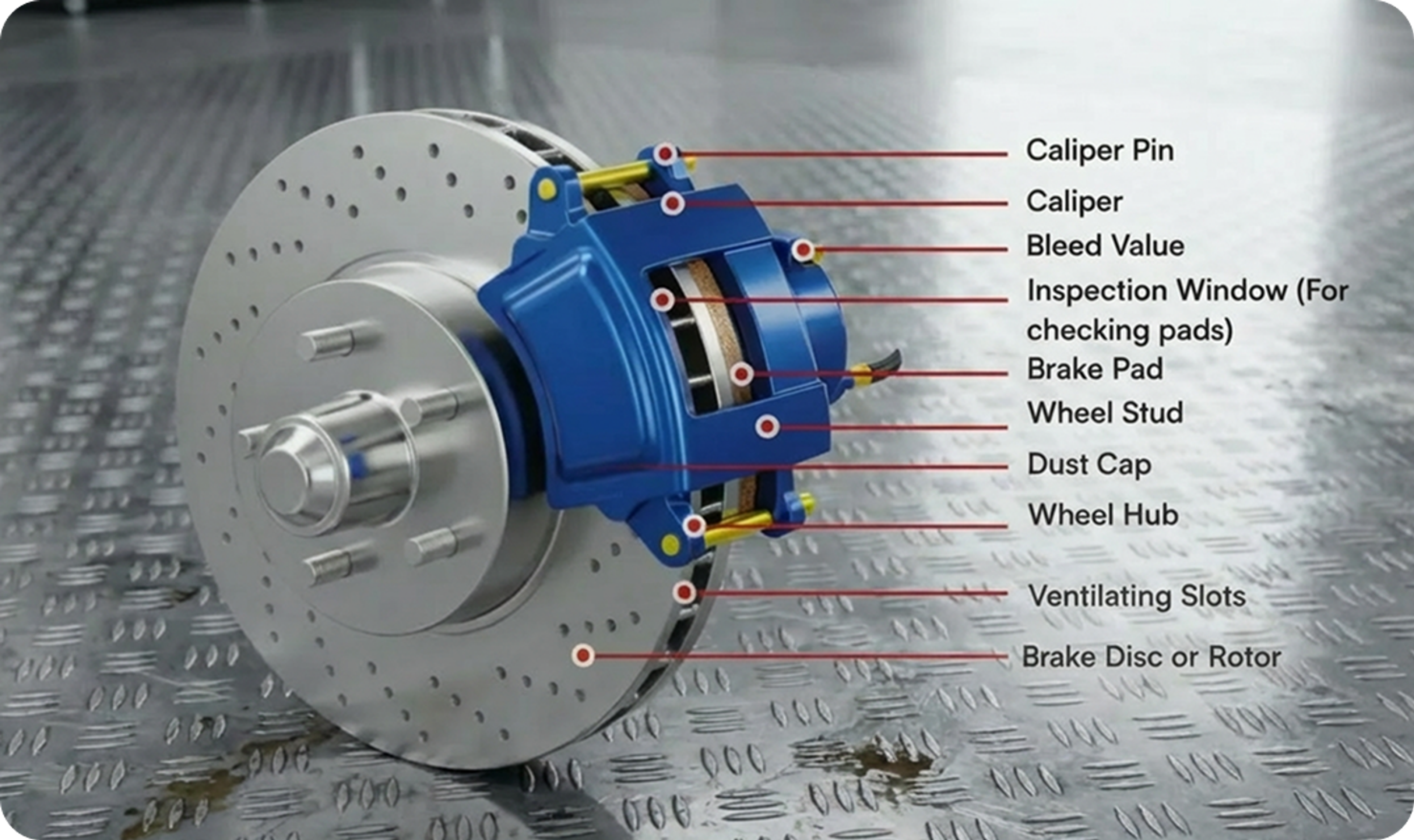
In a disc brake, a rotating brake disc is firmly connected to the wheel and turns with it. When the brake pedal is pressed, braking force is transmitted—in most vehicles hydraulically—from the master cylinder to the brake caliper via the brake lines.
The brake caliper contains one or more pistons that are activated by hydraulic pressure. These pistons press the brake pads evenly against the surface of the brake disc on both sides. This creates a controlled frictional force that slows down or stops the wheel. The even distribution of pressure ensures stable and easily controllable braking performance.
Heat generation and cooling
The contact between the brake pads and the brake disc converts kinetic energy into heat. This heat is generated every time the brakes are applied and must be reliably dissipated to ensure consistent braking performance.
The open design of the disc brake promotes effective heat dissipation, as the brake disc is directly exposed to the ambient air. In addition, special designs such as ventilated or perforated brake discs can further improve cooling performance. This keeps the braking effect stable even during repeated or heavy braking, reducing the risk of performance loss.

Effects on braking performance
The combination of direct power transmission, even friction, and efficient cooling ensures that disc brakes respond quickly and can be controlled precisely. This has a positive effect on braking distance and overall handling, especially at higher speeds or under increased loads. For this reason, disc brakes are the preferred choice in modern braking systems where safety and consistent performance are paramount.

Advantages of disc brakes
- High and consistent braking performance
- Good cooling thanks to open design
- Consistent braking performance in wet conditions
- Precise dosing
- Stable braking distance even under high loads
Disadvantages of disc brakes
- Higher costs compared to drum brakes
- More susceptible to corrosion during longer periods of inactivity
- Brake pads wear out faster than brake shoes.
Areas of application for our products
Disc brakes are now used in almost all modern vehicle classes, especially on the front axles, where the highest braking forces occur. The disc brake system consists of several coordinated components that work together to ensure reliable deceleration.
- Brake pads: Their job is to slow down the movement of the wheel by creating friction on the disc.
- Brake disc: This serves as a rotating friction surface and is firmly connected to the wheel.
- Brake caliper: This transmits the hydraulic braking force and ensures that the brake pads are pressed evenly against the disc.
The Danaher catalog contains suitable brake pads, brake discs, and brake calipers designed for different vehicle types and applications.

product features
OE specifications
Our discs meet original equipment (OE) specifications and ensure compatibility and reliability.
rust resistance
Our coating provides excellent corrosion protection and outperforms conventional paint or zinc coatings.
Exceptional quality
They undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand extreme conditions. The simplex design ensures quiet operation and long-lasting quality.
Easy installation
Danaher products are precisely matched to a wide range of vehicle makes and models, ensuring easy installation and optimal braking performance.
Find brake pads and calipers for your vehicle
Rely on proven quality, low wear, and reliable braking performance for greater safety on every journey.
Maintenance and typical problems
Signs of wear
Worn brake pads often make themselves noticeable by squeaking or grinding. An increased braking distance or a change in pedal feel can also indicate wear. Brake noise is not only caused by wear, but also by dirt, moisture, or unsuitable material combinations between the brake pad and brake disc. Uneven pad wear can also cause vibrations during braking.

Maintenance of brake discs
A pulsating brake pedal often indicates unevenly worn or warped brake discs. This can be caused by high thermal loads or installation errors, among other things. Regular visual and functional checks of the brake system, including brake pads, brake discs, and brake calipers, help to detect damage at an early stage and extend the service life of the brake components.

Why are Danaher brake components a reliable choice?
Reliable quality and durability
All brake products undergo defined quality tests and are designed for different operating conditions. This ensures long-term functionality and high operational reliability.
High safety standards
Danaher products support precise braking force modulation and contribute to stable braking distances. They thus make an important contribution to the safety of the entire vehicle.
Precise fit for many vehicle types
The brake components are designed to fit a wide range of vehicle makes and models. The exact fit makes installation easier, reduces malfunctions, and ensures even wear in the brake system.
FAQs about our brake discs
Although our products are designed for easy installation, we recommend having them installed by a professional mechanic to ensure correct and safe installation.
Maintenance and typical problems
signs of wear
Worn brake pads often make themselves noticeable by squeaking or grinding. An increased braking distance or a change in pedal feel can also indicate wear. Brake noise is not only caused by wear, but also by dirt, moisture, or unsuitable material combinations between the brake pad and brake disc. Uneven pad wear can also cause vibrations during braking.
Maintenance of brake discs
A pulsating brake pedal often indicates unevenly worn or warped brake discs. This can be caused by high thermal loads or installation errors, among other things. Regular visual and functional checks of the brake system, including brake pads, brake discs, and brake calipers, help to detect damage at an early stage and extend the service life of the brake components.
